Introduction to Databases
A database can be considered as a collection of tabels.
Tables are made of rows and columns.
Columns have names by which they can be accessed.
Each record is stored as a row in a table.
What is SQL?
- SQL stands for Structured Query Language.
- It is used to communicate with and manage databases.
Statements in SQL
In SQL, statements are categorised into one of the 5 categories.
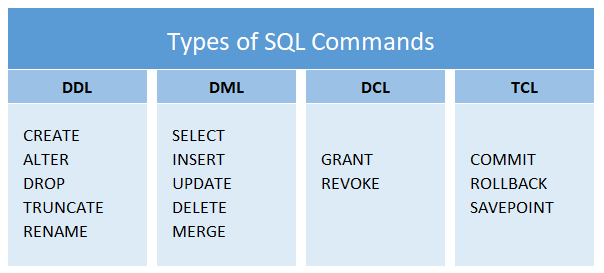
As this is a beginners guide, we will go over the basic statements:
CREATE, DROP, TRUNCATE, INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, SELECT
CREATE
Create command is used to create a Table in a database.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE <TABLE_NAME> (
<col_1_name> <datatype>,
<col_2_name> <datatype>,
<col_3_name> <datatype>,
.
.
<col_n_name> <datatype>
);
here <TABLE_NAME> is the name of the table. <col_n_name> is the column name and <datatype> is the datatype of the cossusponding column.
Example:
CREATE TABLE student (
name varchar(50),
roll_no int,
marks int
);
In the above example we are creating a new Table named student.
The table contains three columns: name, roll number and marks
Name is defined as varchar(50) . This datatype is used to store text data (strings) of length 50. ie it can store at max 50 characters.
roll_no and marks are defined as int which stands for integer which can be any number, positive or negative.
INSERT
currently table student is empty.
In order to add data to this table we use the INSERT command.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO <TABLE_NAME> (<col_1_name>, <col_2_name>, <col_3_name>, ...)
VALUES (<value_1>, <value_2>, <value_3>, ...);
OR
INSERT INTO <TABLE_NAME> ()
VALUES (<value_1>, <value_2>, <value_3>, ...);
Here, <TABLE_NAME> is the name of the table. The column names and corresponding values are listed in parentheses.
Example:
INSERT INTO student ()
VALUES ('John Doe', 1, 85);
In the above example, we are adding a new row to the student table with name as 'John Doe', roll_no as 1, and marks as 85.
SELECT
Now that we have data in our table, we can retrive this data and print to screen.
For this the SELECT command is. Using the select command we can query the database and see the results.
SYNTAX:
SELECT <column1>, <column2>, ...
FROM <TABLE_NAME>;
-- OR
-- In the following command * sign represents all columns
SELECT * FROM <TABLE_NAME>;
-- OR
-- Use this syntax when specific data is needed
SELECT <column1>, <column2>, ...
FROM <TABLE_NAME>
WHERE <condition>;
Example:
SELECT name, marks
FROM student;
This example retrieves the name and marks of the student with roll_no 1.
In order to select name students with marks more than 60 we can use the following command
SELECT name FROM student WHERE` marks > 60;
Or we can print all data of all students (all records)
SELECT * FROM student;
UPDATE
The UPDATE command is used to modify existing records in a table.
this can be used to fix errors or update information in the table.
SYNTAX:
UPDATE <TABLE_NAME>
SET <column1> = <value1>, <column2> = <value2>, ...
WHERE <condition>;
Example:
the marks of a student with roll_no 7 was set as 18 by mistake.
The actual marks of the student is 81.
The following query can be used to make this change
UPDATE student
SET marks = 81
WHERE roll_no = 7;
DELETE
The DELETE command is used to remove records from a table.
SYNTAX:
DELETE FROM <TABLE_NAME>
WHERE <condition>;
Example:
DELETE FROM student
WHERE roll_no = 1;
This example deletes the record of the student with roll_no 1.
DROP
The DROP command is used to delete a table or database.
If a table is no longer required we can remove it from the base.
SYNTAX:
DROP TABLE <TABLE_NAME>;
Example:
DROP TABLE student;
This example deletes the student table.
TRUNCATE
Instead of deleting the complete table, sometime we just wanna remove all data from the table but keep the table structure (columns).
The TRUNCATE command is used to remove all records from a table but keeps the table structure.
SYNTAX:
TRUNCATE TABLE <TABLE_NAME>;
Example:
TRUNCATE TABLE student;
This example removes all records from the student table but keeps the table structure intact.
Summary
CREATE: Creates a new table.INSERT: Adds data to a table.SELECT: Retrieves data from a table.UPDATE: Modifies existing data in a table.DELETE: Removes data from a table.DROP: Deletes a table or database.TRUNCATE: Removes all records from a table but retains the table structure.